Introduction: The Rising Threat of Business Email Compromise
In today’s digital landscape, Business Email Compromise (BEC) has become one of the most dangerous and costly cybersecurity threats for organizations globally. This advanced form of social engineering takes advantage of trust and authority within company email communications, enabling attackers to deceive employees, vendors, or executives into disclosing sensitive information or approving fraudulent wire transfers.
By 2025, BEC attacks have escalated by over 30%, making them a critical concern for businesses prioritizing email security and safeguarding their financial and data assets. These attacks not only compromise email accounts but also disrupt operations and cause financial losses averaging millions per incident.
To counteract these evolving threats, understanding attack methods, spotting warning signs, and deploying robust measures like security awareness training and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are vital. With tactics ranging from CEO fraud to vendor email compromise and phishing, staying informed is your best defense against becoming another BEC statistic.
While BEC emails are often hard to detect because they bypass typical spam filters, keeping your inbox clean and focused can help reduce distractions and potential risks. Cleanfox helps you eliminate spam and unwanted emails, so you can stay alert to what really matters.
Understanding Business Email Compromise (BEC)
What Is BEC?
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of cyberattack where attackers—often organized cybercriminal groups—target organizations by exploiting the trust inherent in business email communications. Unlike traditional phishing attacks that send out generic messages, BEC scams are highly targeted and sophisticated. They rely on social engineering tactics to impersonate trusted contacts within your company—such as executives, partners, or third-party vendors—to deceive employees into making unauthorized wire transfers, sharing sensitive data, or performing other actions that benefit the attacker.
These emails often appear legitimate, sometimes even compromising existing email accounts to make them virtually indistinguishable from authentic correspondence.
BEC attacks typically do not involve malware or malicious links. Instead, they exploit employees’ trust and sense of urgency. Attackers spend significant time profiling your business, identifying key personnel, and customizing their approach to maximize impact. This makes BEC a stealthy, high-impact threat, costing businesses billions annually through deception, not code.
Common Types of BEC Scams
While every BEC attack is tailored to exploit your company’s unique vulnerabilities, several recurring schemes have emerged as particularly effective for threat actors:
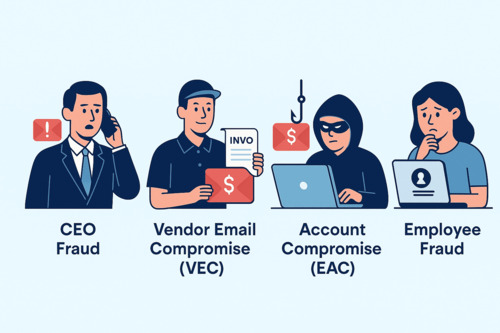
- CEO Fraud: Attackers impersonate your CEO or another senior executive, urgently requesting wire transfers to a fraudulent account—often under the guise of a confidential or time-sensitive transaction.
- Vendor Email Compromise (VEC): The attacker poses as a trusted vendor or supplier, sending fake invoices or requesting payments to be redirected to a new, attacker-controlled bank account.
- Account Compromise (EAC): Attackers gain unauthorized access to a legitimate email account—possibly through phishing or credential theft—and use it to request sensitive information or direct financial transfers. This is especially difficult to detect since the emails originate from a genuine internal or partner address.
- Employee Fraud: In this scheme, an employee is deceived into changing payroll details or making payments to an external party, often under the pretense of a routine business process or an executive request.
These schemes are constantly evolving, with attackers leveraging generative AI and more advanced social engineering tactics to create increasingly convincing lures. The impact goes beyond financial losses—BEC attacks can expose sensitive company and customer data, erode trust, and even pave the way for further security breaches.
Recognizing these tactics is the first step toward building effective defenses and safeguarding your organization against the next wave of BEC threats.
How to Spot a BEC Attack
Warning Signs of BEC
Spotting a Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack before it causes damage can be challenging, but several warning signs can help you identify potential threats. One of the most glaring indicators is unusual or unexpected requests related to wire transfers or the sharing of sensitive business information that deviate from your company’s normal procedures. Attackers often craft emails that closely mimic legitimate invoices or payment requests, making them convincing enough to fool even experienced staff—especially those who regularly handle financial transactions.

Another red flag is sudden, urgent demands for confidential data or noticeable changes in communication patterns. These anomalies can signal a BEC attack in progress, warranting immediate attention.
Other warning signs include generic greetings instead of personalized salutations, suspicious email sender addresses that resemble but are not identical to known contacts, and unexpected attachments or links that prompt action without adequate explanation. These subtle clues often expose attempts to compromise your company’s data or gain unauthorized access to email accounts.
Behavioral and Technical Indicators
Beyond content clues, behavioral anomalies can often indicate that an email account or employee has been compromised. For instance, an internal account suddenly sending messages at odd hours, reaching out to recipients it doesn’t normally contact, or displaying a drastically different communication style—such as informal language from an executive known for precise communication—are strong signs of a BEC email compromise.
On the technical side, detecting anomalous sending behaviors can be important. These include spikes in email traffic from specific accounts or messages originating from geographic locations unfamiliar to your employee base. Monitoring these factors can help uncover the subtle methods attackers use to bypass traditional defenses.

Pairing behavioral analysis with cybersecurity tools strengthens your defense against social engineering and hard-to-detect threats.
Identifying behavioral and technical signs early helps your team respond fast, reduce risk, and protect sensitive company data.
Preventative Measures and Mitigation Strategies
Say goodbye to spam, clutter, and chaos.
Our smart email cleaner filters out junk, organizes your inbox, and helps you focus on what really matters.
✅ Block spam automatically
✅ Organize emails by priority
✅ Keep your inbox clean
✅ Clean old emails you don’t read
📱 Available on the App Store and Google Play.
Implementing Robust Security Protocols
Securing your business against business email compromise (BEC) attacks begins with a multi-layered security approach. One of the most effective defenses is enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all email accounts and business applications. Multi-factor authentication significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if attackers obtain valid credentials.
Regularly scan systems for malware, phishing, and suspicious forwarding rules attackers use to maintain hidden access—even after authentication. Establish strict, multi-step approval processes for all sensitive transactions, especially wire transfers, requiring verification outside the original email channel. For example, confirm payment instructions with vendors or partners by phone or in person before processing any changes.
Use advanced filtering, encryption, and real-time monitoring to detect anomalies and block malicious emails before they reach employees.
Employee Training and Awareness
No matter how strong your technical controls, your business remains vulnerable if employees are not equipped to recognize and resist social engineering tactics. Regular, targeted security awareness training helps your team understand the hallmarks of BEC scams, phishing emails, and other common attack vectors. Equip employees with practical skills—such as verifying sender addresses, questioning urgent or unusual requests, and knowing how to report suspicious communications.

Stress the importance of never sharing sensitive data or complying with financial requests without proper authorization. Building a security-focused culture turns your team into the first line of defense against email threats and social engineering.
Incident Response Planning
Even with the best preventive measures, it’s critical to prepare for the possibility of a BEC attack. Create a BEC-specific incident response plan—speed is critical, especially when financial assets are at risk.
Your plan should clearly define roles, escalation paths, and communication protocols, ensuring rapid engagement with financial institutions and law enforcement to attempt to halt fraudulent wire transfers or undo unauthorized payments. Preserve all evidence, such as email logs and IP access records, to support investigations and insurance claims.

After an incident, conduct a thorough post-mortem to identify vulnerabilities, update procedures, and reinforce training—turning each event into a lesson that strengthens your organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
By combining robust technical controls, ongoing employee education, and proactive incident response planning, you can significantly reduce your risk of business email compromise and minimize the impact of any successful attack on your company.
Conclusion: Staying a Step Ahead of BEC Criminals 💡
Business Email Compromise (BEC) continues to be a rapidly growing and costly threat for organizations of all sizes. Millions are lost daily to increasingly sophisticated scams. To safeguard your company, implement strong security measures such as multi-factor authentication. Provide ongoing security awareness training for employees. Establish a clear and actionable incident response plan. By staying vigilant and proactive against evolving social engineering tactics, you can protect sensitive data.
You also reduce the risk of expensive wire transfer fraud and maintain the trust of partners and customers.
For a broader overview of the attacks businesses face daily, check out our guide on Email Threats: The Most Common Email Attacks — a detailed look at the tactics cybercriminals rely on.
Don’t wait—take immediate steps to defend your business against BEC attacks today.
FAQ 📖
What is Business Email Compromise (BEC) and how does it operate?
BEC attacks trick employees using fake identities—not malware—making them harder to detect and financially devastating. It operates through phishing, social engineering, and sometimes hacking legitimate email accounts. By exploiting trust within organizations, attackers can cause significant financial losses.
What are the most common tactics scammers use in BEC attacks?
Scammers frequently rely on tactics like email spoofing or using compromised accounts to impersonate executives, vendors, or other trusted contacts. They often create a sense of urgency or use subtle domain changes to trick employees into bypassing verification steps. These methods are designed to prompt urgent payments or the sharing of sensitive data.
How can businesses identify and prevent falling victim to BEC scams?
Email authentication protocols like DMARC, SPF, and DKIM help block spoofed emails and prevent BEC attacks. Use AI-driven email filters and train employees to recognize suspicious emails and social engineering tactics. Verify fund requests via a second channel and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access.
Who within an organization is most vulnerable to Business Email Compromise attempts?
HR and finance staff face higher BEC risk due to their access to sensitive financial and personal data. Strengthening security protocols in these areas is critical to reducing risks.
Enjoyed this article? Dive deeper into email security with our post: “What Is Email Bombing? How to Stop It.” Don’t forget to browse our blog for more useful tips and insights.